Contents
Early Detection Methods
Early osteoarthritis detection is difficult, it is a degenerative joint disease that can begin early in life. However, the changes in articular cartilage are usually only detected after the patient begins to experience pain. This may be years or even decades after the initial cartilage injury.
Unfortunately, joint pain is usually a sign of advanced joint destruction. However, early osteoarthritis detection makes it possible to slow its development. There are some tests that can be done to determine if individuals are developing osteoarthritis.
Imaging and Arthroscopy for Detection of Osteoarthritis
During an injoint xray arthritisitial consultation, the patient will be asked about their medical history and a function joint test is performed. This can provide the doctor with an indication of the possible cause of joint disease. However, to get a better understanding of the condition, imaging procedures are often performed on the joint(s) causing concern.
Joint X-rays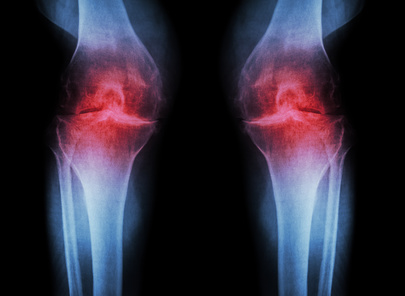
Often one of the first examinations will involve an x-ray. These radiographs can capture the dense structures of the bones. Early damage to the cartilage is not detectable by x-ray absorption as cartilage and soft tissue remain invisible. However, x-rays can detect problems associated with advanced joint arthrosis by identifying narrowing of the joint spaces or bone deformities1.
Some specialists point-out that if an x-ray is going to be used to determine joint space it must be measured correctly under load. Thus, the radiograph should always be taken standing up to correctly identify the joint line.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Other imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasounds can also be used to detect joint diseases. The advantage of these methods is that they don’t release radiation and they capture visible soft tissue and cartilage. The problem with this technique is that it can be difficult to distinguish between arthritis and osteoarthritis. Inflammatory processes and conditions within the synovial fluid cannot be properly diagnosed by imaging techniques alone.
Arthroscopy
The most effective way to correctly diagnose joint diseases is through a minor surgical procedure called arthroscopy. This involves making a small incision at the sight of the affected joint and using a probe to examine the joint condition. A sample of synovial fluid is usually obtained for testing for inflammatory markers. This can help to differentiate between arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthroscopy also allows for joint-preserving measures to be performed. This may include smoothing cartilage surfaces or remove bone fragments.
Bibliography:
“Arthritis” is a term used to describe a wide range of conditions that negatively impact the musculoskeletal system. The word arthritis is Greek for joint inflammation, one of the defining symptoms of the disease.
With more than 100 different variations of the disease, there are also slight differences in symptoms.
Overarching Arthritis Symptoms
All patients suffering from arthritis will experience some level of discomfort and pain. Arthritis pain varies in severity and duration depending on the underlying cause, disease progression, and trigger events. Other common symptoms associated with arthritis include: Joint stiffness
- Sutter et al. 2012. “New Developments in hip imaging.” Radiology. 264(3):651-67 ↩






